A dissertation, thesis, or research paper is identified as a lengthy and complex piece of academic writing formulated on the basis of the original research conducted by a student and submitted for the successful completion of a Ph.D., master’s, or bachelor’s degree.
A dissertation paper is perhaps the most elongated piece of writing a student has to develop and it often gets quite daunting because of the confusion about the commencing point. This article will help you to understand what exactly should be a part of your dissertation and what should be eliminated.
Adopting a suitable structure for your dissertation assignment
It is important for a student to know that not all the dissertation papers are structured in a similar manner. It depends largely upon the topic, set-up location, approach, and discipline your research is associated with.
For instance, the structure of a dissertation paper related to the field of humanities is similar to the format of a long essay which starts with an introduction developing an overall argument eventually to encourage the chief thesis, with additional chapters focusing on the diverse case studies or themes.
However, if on the other hand a scholar is conducting an empirical research in a subject area related to science or social science, the dissertation paper will generally contain all the common elements like an introduction, abstract, literature review, methodology, conclusion, etc. In most of the structures each of this is included in a different chapter, but in some a scholar might be asked to combine them. For instance, in some qualitative social science dissertation paper structures the results and discussions are put together rather than presented as separate chapters.
The order of different chapters in a dissertation paper may vary as per the universities, nations, or disciplines. For example, in certain universities it is suggested to always add the conclusion section prior to the discussion chapter. It is highly recommended for a student to carefully analyze the department’s guidelines or reach out to his university mentors or supervisors immediately if he has any query about the structure of the paper.
Take a look at sections that are most commonly found in the dissertation assignments
Title Page
The opening leaf of a dissertation document includes the title of the paper, name of the student, department name, name of the university or college, an appellation of the degree discipline, and the submission date. In certain scenarios, it also contains the identification number of the scholar, supervisor or professor’s name, and the logo of the institution. Several universities have a rigid requirement list when it comes to formatting the dissertation title page.
The title page of a dissertation is sometimes also followed by an approval page that is signed by the project head and other committee members of your academic institution. Many times, students are also asked to write the term ‘partial fulfilment’ on the title page of their dissertation to highlight that the research document was one of the several requirements completed by you to obtain your degree. Keep in mind that the title page does not have a page number.
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgments is an optional chapter in a dissertation paper which allows a scholar with space to thank everyone who supported and assisted him throughout the journey of developing an impactful paper. The list can include the supervisors, family members, friends, and research participants.
Here are a few things you should always consider while writing the acknowledgments for your dissertation:
- Requirements of your academic institution.
- Adding a touch of humor at relevant places.
- Showing gratitude towards the right people from your institution as well as personal life.
- The chapter should be of appropriate length.
Abstract
Abstract is defined as a brief outline of the entire dissertation paper. It is usually only about 150-300 words long. It is advised that a student should write the abstract after he has completed the rest of the sections thoroughly. The important elements which should be included in this chapter are:
- The main theme and objective of the dissertation.
- A description of the methodology used in the procedure.
- A synopsis of the results obtained.
- A quick look into the derived conclusions.
Although an abstract is terse in nature, it is the foremost and, in some cases, the only section of a dissertation paper that the readers will read. Therefore, it is essential to approach it accurately. If a student is struggling to draft a persuasive abstract for his dissertation paper, he can simply refer to the handbook on how to write an abstract on the livewebtutors platform.
Index or Table of Contents
In the index or table of contents, a student is supposed to list out all the chapters, their sub-topics, and their respective page numbers. The dissertation contents page provides a reader with an overview of the dissertation structure and assists him to easily navigate through the paper.
A table of contents is a significant section to be presented at the beginning of your dissertation for two major reasons.
- It will help the readers as well as your mentors to easily locate the contents of particular topics presented as chapters or subtitles.
- It will help you as a writer to arrange your work in an organized manner so that none of the important sections from your dissertation are left out.
Keep in mind that the page number for an index is always centred at the bottom of the page in Roman numeral form.
A Record of Figures and Tables
If a student has included numerous tables and illustrations in his dissertation paper, it is ideal to specify them in a properly numbered list. This list can also be generated automatically by using the ‘Inset Caption’ feature in the Microsoft Word.
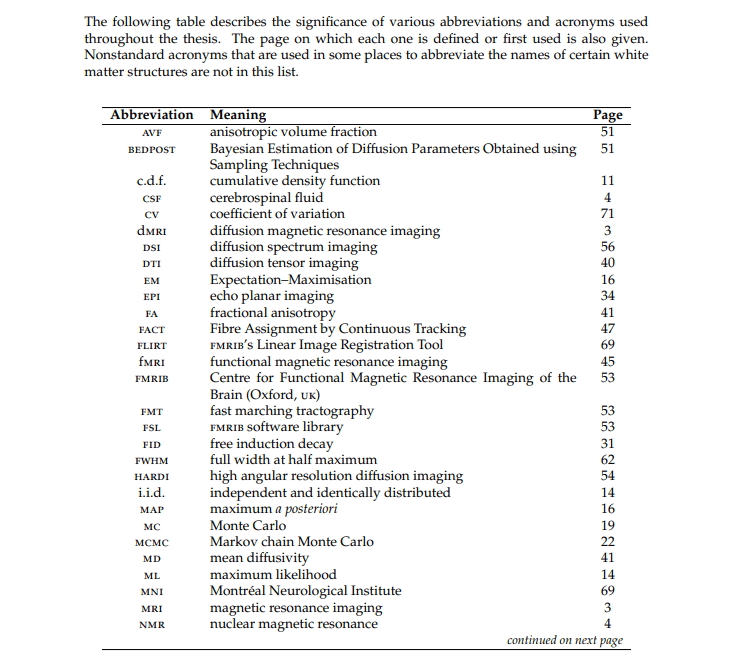
An Inventory of Abbreviations
If a dissertation paper includes several acronyms it is only a smart move to include those in an alphabetized list of abbreviations so that the readers can smoothly locate their meanings.
If you plan to add a list of abbreviations to your dissertation, it is only logical to add them near the beginning of your research document, preferably after the table of contents. Do not forget to mention your list of abbreviations in the index section so that your readers can know about its existence.
There is no need to add common abbreviations in this inventory as they will unnecessarily overload the list with the terms that your readers are already aware of and eventually discourage them from accessing the list altogether.
Glossary
If a dissertation paper includes a large number of specialized terminologies that a reader might not be aware of, it is only accurate to include a glossary. This part of a dissertation paper includes an alphabetical list of such terms and further explains each of them with a short definition or description.
A glossary can help the readers of your dissertation to take a quick look at the key terms of your dissertation before they begin to actually read your content in full. If there are only a few terms that need an explanation, there is no need to add a glossary section as they can be presented in the footnotes of the dissertation. Remember that abbreviations cannot be a part of your dissertation glossary.
Introduction
It is in this chapter of the dissertation that a student introduces the topic or theme, states the aim of the paper, determines its significance in today’s times, and informs the readers what lays ahead in the dissertation document. An introduction chapter should successfully:
- Establish the research topic of your paper by providing relevant background information to adequately ponder your efforts.
- Confine the focus on a specific aspect of the topic and hence express the scope of the dissertation.
- Examine the position of prevailing research on the theme, highlighting the importance of your dissertation to a bigger problem or argument.
- State coherently the research questions and purposes.
- Provide a perfect overview of your dissertation’s structure.
Each and every word of the introduction should be lucid, involving, and pertinent to the dissertation research. After being through with the reading of the introduction chapter, a reader should be able to clearly grasp the what, why, and how of the presented dissertation paper. To know more about the introduction chapter, read the livewebtutors platform’s guide on how to write a dissertation introduction.
The Review of Literature or Theoretical Framework
Before a student conducts research for his dissertation assignment, he needs to start on the literature review to develop an in-depth understanding of the studies that already exist on the selected theme. This requires:
- Gathering credible sources, such as books, articles, journals, etc., and decide on the most fitting ones.
- Crucially assessing and examining each source.
- Establishing relations between the theme, pattern, gaps, and conflicts to state a strong point.
In the dissertation literature review chapter or section, a scholar should not only provide a synopsis of the existing studies but also develop an intangible arrangement and case that will eventually lead to a well-defined basis for his own research. For instance, a literature review might aim to present how the dissertation:
- Acknowledges the disparity in the literature.
- Presents a new academic or procedural approach to the dissertation topic.
- Suggest a solution to the unanswered questions.
- Evolves a theoretical debate.
- Develops and reinforces the existing knowledge with new information.
Literature review often form the basis for the theoretical framework in which a student evaluates and defines the major theories, concepts, and models that surrounds his dissertation. It is in this chapter that a student can effortlessly provide answers to all the descriptive research queries about the affiliation between the variables or concepts.
Methodology
The methodology segment of a dissertation focuses on how the scholar has conducted the research for his assignment, thereby allowing the readers to appraise its rationality. the methodology section of a dissertation should generally include:
Details about the overall research approved and the type of research conducted for gathering data for the dissertation paper.
- Niceties about the methods of collecting data such as interviews, surveys, and archives.
- Particulars of where, when, and whom of the resort procedure.
- The methodology used to scrutinize the collected data. It can either be statistical analysis discourse analysis, etc.
- The various apparatuses and supplies used in the research process.
- A brief discussion of any hurdles that occurred in the scholar’s way of conducting the elaborate research and how the student tackled them.
- An analysis or justification of the used methodology.
The ultimate aim of the methodology section in a dissertation is to appropriately report what exactly a student did as well as convincing the readers that why his approach was apt in answering the mentioned research questions.
Results
The next course of action is to set forth the results of your research. A student can structure this segment of his dissertation paper around the sub-questions, topics, or the hypothesis. A scholar should ensure that he only accounts for the results that are associated with the aim and the research questions of the dissertation paper. In some programs, the results chapter is Quickly included separately from the discussion section while in some disciplines that you are often combined together.

For instance, in a dissertation following qualitative methods such as in-depth interviews, the data presented is usually combined with the discussion and analysis section while in a dissertation supporting quantitative and experimental methods the results are presented in a separate segment prior to discussing their underlying meaning. If a student is confused with this combination or so, he should consult his university mentors and take a look at the sample dissertations to determine the best structure for his dissertation paper.
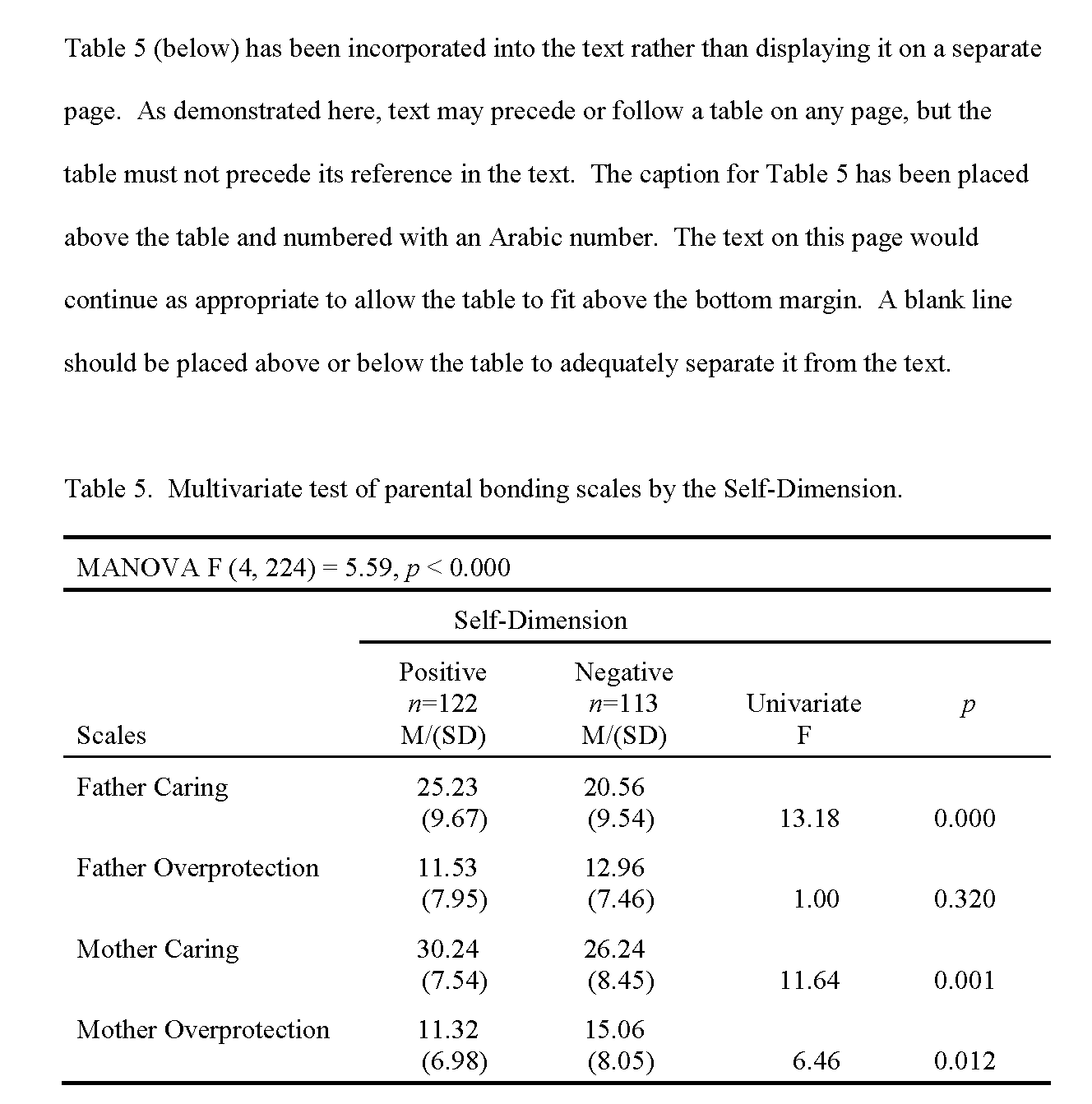
It is only relevant to include graphs, charts, and tables inter results chapter of a dissertation. A student should spend some time thinking about how he can present the collected data neatly and flawlessly for better readability of the same. He should not include figures or charts just to repeat what he has already written. The illustrations should tend to provide some extra details or should practically envision the results in a way that enhances the value of the dissertation assignment.
The complete version of the collected details interview transcript questionnaires attack truck can be included in the appendix section of the dissertation paper
Discussion
The discussion chapter of a dissertation is where a student discovers the sense and insinuations of the gathered results in reference to the research questions. In this section, the scholar interprets the results in great detail and further confers whether they meet his dissertation objectives and how they suit the framework that was established in the previous sections of the dissertation. If any of the derived results are unexpected, the student should offer an explanation for what may be the reason behind this. It is a smart idea for a student to take into account the substitute readings of the gathered data and discuss any obstacles that might have affected the results.
The discussion chapter should considerably refer to other academic work to represent how the derived results sit with the existing knowledge. Many a time this section also includes suggestions for future studies or practical actions.
Conclusion
A dissertation conclusion should be designed in such a way that it precisely answers the key research question, providing the reader with an obvious understanding of your main argument.
In certain academic areas, the conclusion Is equivalent to a brief section that is included just before the discussion section in a dissertation. This means that a scholar will first state the overall conclusions and then proceed to discuss them in detail and decipher their meaning.
In some other conventions, conclusion chapter refers to the final chapter of the dissertation where the scholar winds up his paper with a final look at what he did and how he did it. This type of conclusion often includes suggestions for future studies or practices.
It is important for a student to show how his findings contribute positively to the field of knowledge and why his dissertation is valuable in the conclusion chapter. This segment basically focuses on what the scholar has added to the already known facts.
Reference List
It is essential to add complete details of all the sources that a student has referred to in a properly structured reference list, also known as a bibliography or the works cited list. It is essential to follow a suitable citation style or reference style acceptable by the university of the scholar while presenting the cited data. Each of the reference styles has a strict and specific format for how to mention the sources in the reference list.
The most frequently used reference styles are the APA and MLA methods but it depends on a student’s program or the mentor to specify which citation technique should be used in the dissertation paper. If unsure, check the guidelines or ask your supervisor immediately.
Appendices
A dissertation paper should only include material that straightforwardly assists in answering the pre-formed research question. The documents that a scholar has used do not fit into these essential materials and therefore are not fit to be a part of the main dissertation paper. Therefore, all the interview transcripts or survey questionnaires or full figure tables should be a part of the appendices section.
Editing and Proofreading
Ensuring that all the chapters of a dissertation are in the right order is the foremost step to firmly edit a dissertation paper. A student should spare enough time for editing and proofreading the prepared assignment.Grammatical errors, punctuation mistakes, and sloppy blunders can often degrade the quality of the perfectly worked upon dissertation paper.
Be open to write and revise several drafts of your dissertation paper before focusing on language mistakes, typographical errors, and other discrepancies.