The focus was on a star network. A star network has just one hub, and a Star topology is a star-like structure. A central hub or switch connects each computer in the study's star architecture. A seat links all standards, and the centre hub connects network nodes.
The experiment goes on to show the advantages and disadvantages of star networks. The centralization of a star network simplifies use while isolating each device. Cons: Network transmission in a star design is highly centralized. The network collapses if the central hub fails.
In the home and office, star networks are standard. It is possible to save all important data backups on the hub in a hidden folder so that if one computer fails, the data may be retrieved by another. This network provides more privacy than any other.
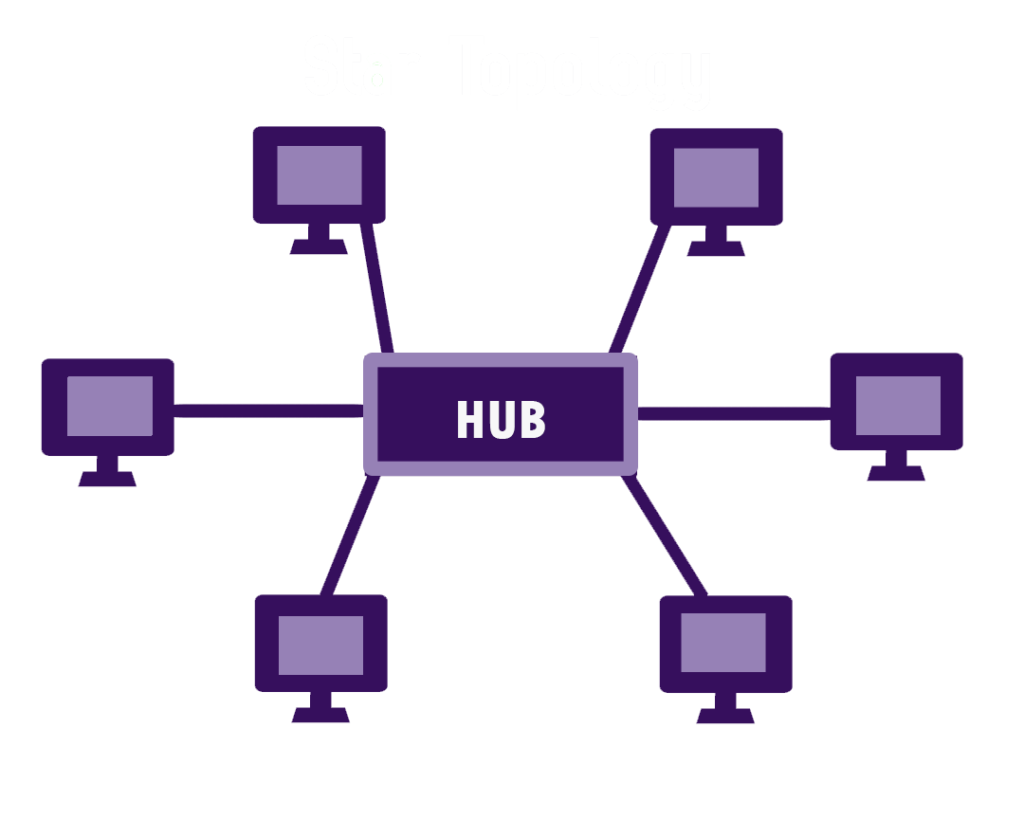
The primary purpose of this study is to evaluate the star network design. Its physical structure. (http://www.yourdictionary.com/telecom/star-topology) A network contains a central node to which all other devices connect and communicate. Star-shaped hub, leaf nodes, and transmission lines
A hub links a file server, workstation, and peripherals. DATA CENTRE HANDLING An arriving packet is sent to all associated nodes, but only one delivers it correctly. Data from a star network travels through a hub. Torqued pair, coaxial, and fibre optic connections link computers. Star topologies commonly use twisted-pair copper wire. The seat is connected to one end and the LAN card.
The star topology's centralization makes network management more effortless. Because the hub is the network's heart, any problem can damage the entire network. As a single point of failure, the hub simplifies troubleshooting but increases reliance. Easy to maintain central function
The problems of star topology: The hub is the network's heart. It is possible to save all important data backups in the corner in a hidden folder so that if one computer fails, the data may be retrieved by another.
The researcher discusses the benefits, drawbacks, and uses of star topology. Three concepts drive this project.
- 3.1 Advantages of Star Network
- 3.1.1 Device isolation: Each device is isolated via its hub connection. This facilitates device isolation. This separation also prevents network breakdowns. A cable failure separates just the central computer's workstation in a star network. Except they can't communicate with the isolated workstation. Star network (en.wikipedia.org)
(3) Ease The topology is easy to comprehend—no need for complex routing or message transmission techniques. Notably, isolation and centralization allow for separate defect detection. Having a centralized topology simplifies operation. Star network (en.wikipedia.org)
- 3.1.3 In a star design, each network device has its home run of cable back to a network hub. A cable fault seldom affects the rest of the network. Twisted pair copper cable is widely used in star topologies. Only a few gadgets will result in high data rates. Only for short trips. fallsconnect.com/topology.htm#a
- 3.1.4 Adding new PCs or devices is easy: The star network architecture works with distributed computers. Computer hacking is easy. Extend a connection from the hub to add new devices or nodes. Any computers on the network may access a printer or fax machine connected to the nucleus. Every machine doesn't have a device. Easy to maintain central function if the computers are close enough to the vertices. Defective machines won't affect the entire network. (http://searchnetworking.techtarget.com/dictionary/definition/what-is-star-network.html#)
All computers are connected to one node in instar topologies, reducing network failure risk. So all computers can only communicate via the central node. Censorship gains Enlarging or adding devices to the star may scale the network. Because it's major, it's easy to monitor the network. Adopt suspicious behaviour (http://www.buzzle.com/articles/advantages.html).
If the hub fails, the entire network may be at fault. A single point of failure simplifies troubleshooting, but it also increases reliance on that single point.
- 3.1.7 The star network avoids redundant data packets. In this design, two devices may communicate with up to three devices and two connections. The heavy network utilization by one device does not damage the other devices if the central hub has enough capacity. This means data packets are transported quickly. All computer terminals are directly connected (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Star net). Simple installation is made possible by the flexible cable and modular connection.
- 3.2 Disadvantages Of Network Disabilities
3.2.1 Disabled nodes in case of the hub or concentrator failure. The fundamental disadvantage of a star topology is the central hub. In contrast to the loss of a single link, the central hub failure disables the whole network, instantly isolating all nodes. multiple network topologies (http://www.buzzle.com)
It affects the network's performance and scalability. The number of hub connections and throughput restrict network size and performance. Others may suffer performance deterioration if traffic to another node absorbs a high part of the central node's processing capacity (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Star network).
The system wiring may be complicated.
- 3.2.3 The star topology has one flaw: It fails because the hub links every machine on the network, preventing computers from communicating.
- 3.2.4 Star topology necessitates longer. Extending the network needs extra cables, which complicates the installation.
- 3.2.5 Expensive relative to other topologies: Using a star topology requires a lot of cables, making it the most costly to install. Each computer needs a network cable. A Star Network connection uses unshielded twisted pair (UTP). Star networks also employ RJ45 or Ethernet wires.
- 3.3 Overview On Usage Of Star Network
The star architecture employs 10BASE-T (UTP) cabling and a hub. Network objects are stars connected to the corner. Star systems frequently use Ethernet or local-talk. (http://fallsconnect.com/topology.htm#a)
The most common network topology in households and businesses is a star. The Star Topology uses a hub, a computer or a switch. The main benefit of a star network is that if a cable fails, just one computer is affected.
This pattern is a star. The star network has five workstations, or six if the central computer is one. An individual workstation, the main computer and communications are all represented by spheres. Wireless or wired links?
A star network links all computers to a single hub, and it connects all workstations in a round-about way. Some star networks utilize it as a workstation.
It is best suited for networks with fewer nodes. The hub is the network's heart and must always work and be secure. You may form a "star of stars" network by adding another corner.
It is possible to save all important data backups on the hub in a hidden folder so that if one computer fails, the data may be retrieved by another.
Author: Josef Smith
Studied : Creative Technology at the @University of Twente
Designation : Engineering Analyst ( Associate With LiveWebTutors )


